New Hypothesis on the Origin of Dinosaurs Challenges Traditional Concepts
New Hypothesis on the Origin of Dinosaurs Challenges Traditional Concepts
New Hypothesis on the Origin of Dinosaurs Challenges Traditional Concepts
Jan 27, 2025
Jan 27, 2025
Jan 27, 2025

Dinosaur tracks in southern Utah. Illustrative image. Credit: Getty Images via Canva.
Dinosaur tracks in southern Utah. Illustrative image. Credit: Getty Images via Canva.
Dinosaur tracks in southern Utah. Illustrative image. Credit: Getty Images via Canva.
New research suggests that dinosaurs emerged in the equatorial regions of Gondwana, challenging earlier theories. Discover how this hypothesis could change our understanding of dinosaur evolution.
New research suggests that dinosaurs emerged in the equatorial regions of Gondwana, challenging earlier theories. Discover how this hypothesis could change our understanding of dinosaur evolution.
New research suggests that dinosaurs emerged in the equatorial regions of Gondwana, challenging earlier theories. Discover how this hypothesis could change our understanding of dinosaur evolution.
A recent study from the University College London (UCL) suggests that the first dinosaurs may have originated in the equatorial regions of Gondwana, covering territories that today correspond to the Amazon, the Congo Basin, and the Sahara Desert. This theory challenges previous models that pointed to a more southern origin, in areas such as Argentina, Brazil, and Zimbabwe.
New Perspectives on the Fossil Record
Scientists argue that dinosaurs may have appeared even before the oldest known fossils, which date back approximately 230 million years. To fill gaps in the fossil record, the researchers adopted an innovative approach: rather than interpreting fossil-free areas as places where dinosaurs did not live, they considered these regions unexplored. This implies that evidence of early dinosaurs might be hidden in hard-to-reach locations.
The Competition of the First Dinosaurs
The earliest dinosaurs were small, ranging in size from that of a chicken to a dog. In addition to being bipedal and omnivorous, they had to compete for space with much larger reptiles, such as pseudosuchians, which reached up to 10 meters in length, and pterosaurs, which dominated the skies. The rise of the dinosaurs only occurred after a massive extinction event caused by intense volcanic activity around 201 million years ago, which wiped out many of their competitors.
Expansion and Evolutionary Adaptations
Over time, dinosaurs spread from Gondwana to other continents, such as Europe, Asia, and North America. The researchers suggest that different groups developed specific adaptations to survive in various environments:
Sauropods, like Brontosaurus, remained in regions with warmer climates.
Theropods and ornithischians evolved to generate body heat, allowing them to inhabit cooler areas.
Implications for Dinosaur Evolution
The study also supports an intriguing hypothesis: silesaurids, previously classified only as close relatives of dinosaurs, may have been direct ancestors of ornithischians. If confirmed, this discovery would help fill a gap in the dinosaur evolutionary tree, explaining the absence of ornithischian fossils in the earliest periods.
—
Want to dive deeper? Check out the full article published by UCL!
A recent study from the University College London (UCL) suggests that the first dinosaurs may have originated in the equatorial regions of Gondwana, covering territories that today correspond to the Amazon, the Congo Basin, and the Sahara Desert. This theory challenges previous models that pointed to a more southern origin, in areas such as Argentina, Brazil, and Zimbabwe.
New Perspectives on the Fossil Record
Scientists argue that dinosaurs may have appeared even before the oldest known fossils, which date back approximately 230 million years. To fill gaps in the fossil record, the researchers adopted an innovative approach: rather than interpreting fossil-free areas as places where dinosaurs did not live, they considered these regions unexplored. This implies that evidence of early dinosaurs might be hidden in hard-to-reach locations.
The Competition of the First Dinosaurs
The earliest dinosaurs were small, ranging in size from that of a chicken to a dog. In addition to being bipedal and omnivorous, they had to compete for space with much larger reptiles, such as pseudosuchians, which reached up to 10 meters in length, and pterosaurs, which dominated the skies. The rise of the dinosaurs only occurred after a massive extinction event caused by intense volcanic activity around 201 million years ago, which wiped out many of their competitors.
Expansion and Evolutionary Adaptations
Over time, dinosaurs spread from Gondwana to other continents, such as Europe, Asia, and North America. The researchers suggest that different groups developed specific adaptations to survive in various environments:
Sauropods, like Brontosaurus, remained in regions with warmer climates.
Theropods and ornithischians evolved to generate body heat, allowing them to inhabit cooler areas.
Implications for Dinosaur Evolution
The study also supports an intriguing hypothesis: silesaurids, previously classified only as close relatives of dinosaurs, may have been direct ancestors of ornithischians. If confirmed, this discovery would help fill a gap in the dinosaur evolutionary tree, explaining the absence of ornithischian fossils in the earliest periods.
—
Want to dive deeper? Check out the full article published by UCL!
A recent study from the University College London (UCL) suggests that the first dinosaurs may have originated in the equatorial regions of Gondwana, covering territories that today correspond to the Amazon, the Congo Basin, and the Sahara Desert. This theory challenges previous models that pointed to a more southern origin, in areas such as Argentina, Brazil, and Zimbabwe.
New Perspectives on the Fossil Record
Scientists argue that dinosaurs may have appeared even before the oldest known fossils, which date back approximately 230 million years. To fill gaps in the fossil record, the researchers adopted an innovative approach: rather than interpreting fossil-free areas as places where dinosaurs did not live, they considered these regions unexplored. This implies that evidence of early dinosaurs might be hidden in hard-to-reach locations.
The Competition of the First Dinosaurs
The earliest dinosaurs were small, ranging in size from that of a chicken to a dog. In addition to being bipedal and omnivorous, they had to compete for space with much larger reptiles, such as pseudosuchians, which reached up to 10 meters in length, and pterosaurs, which dominated the skies. The rise of the dinosaurs only occurred after a massive extinction event caused by intense volcanic activity around 201 million years ago, which wiped out many of their competitors.
Expansion and Evolutionary Adaptations
Over time, dinosaurs spread from Gondwana to other continents, such as Europe, Asia, and North America. The researchers suggest that different groups developed specific adaptations to survive in various environments:
Sauropods, like Brontosaurus, remained in regions with warmer climates.
Theropods and ornithischians evolved to generate body heat, allowing them to inhabit cooler areas.
Implications for Dinosaur Evolution
The study also supports an intriguing hypothesis: silesaurids, previously classified only as close relatives of dinosaurs, may have been direct ancestors of ornithischians. If confirmed, this discovery would help fill a gap in the dinosaur evolutionary tree, explaining the absence of ornithischian fossils in the earliest periods.
—
Want to dive deeper? Check out the full article published by UCL!
Compartir en:
Compartir en:
Ver También
Ver También

DeepSeek AI: el chatbot chino que está sacudiendo el mercado global
Feb 7, 2025

Estudio revela que la vida social activa puede reducir el riesgo de demencia
Feb 4, 2025

Año nuevo lunar 2025: la llegada del año de la serpiente
Jan 30, 2025

Nueva hipótesis sobre el origen de los dinosaurios desafía conceptos tradicionales
Jan 27, 2025

Colapso de la plataforma de hielo Conger: alerta para la Antártida Oriental
Dec 20, 2024

Emociones y el cuerpo humano: conexiones milenarias en textos neoasirios
Dec 20, 2024

Un estudio relaciona la contaminación atmosférica con el riesgo de tromboembolia venosa
Dec 20, 2024
Ambiente potencialmente habitable en Marte descubierto por Perseverance
Dec 20, 2024

Revolución XRISM: Nuevos descubrimientos sobre agujeros negros supermasivos
Oct 15, 2024

Estudio aponta que la duplicación del gen AMY1, relacionado con la digestión del almidón, precede a la agricultura
Oct 14, 2024

Nacimientos en la UE caen por debajo de los 4 millones por primera vez desde 1960
Oct 11, 2024

Excavación en Dinamarca revela 50 esqueletos Viking increíblemente preservados
Oct 10, 2024

Estudio detecta mayor incidencia de asma y rinitis alérgica en personas nacidas en otoño e invierno en Finlandia
Oct 9, 2024

Estudio señala similitudes entre la pubertad de adolescentes de la Edad de Hielo y jóvenes modernos
Oct 8, 2024
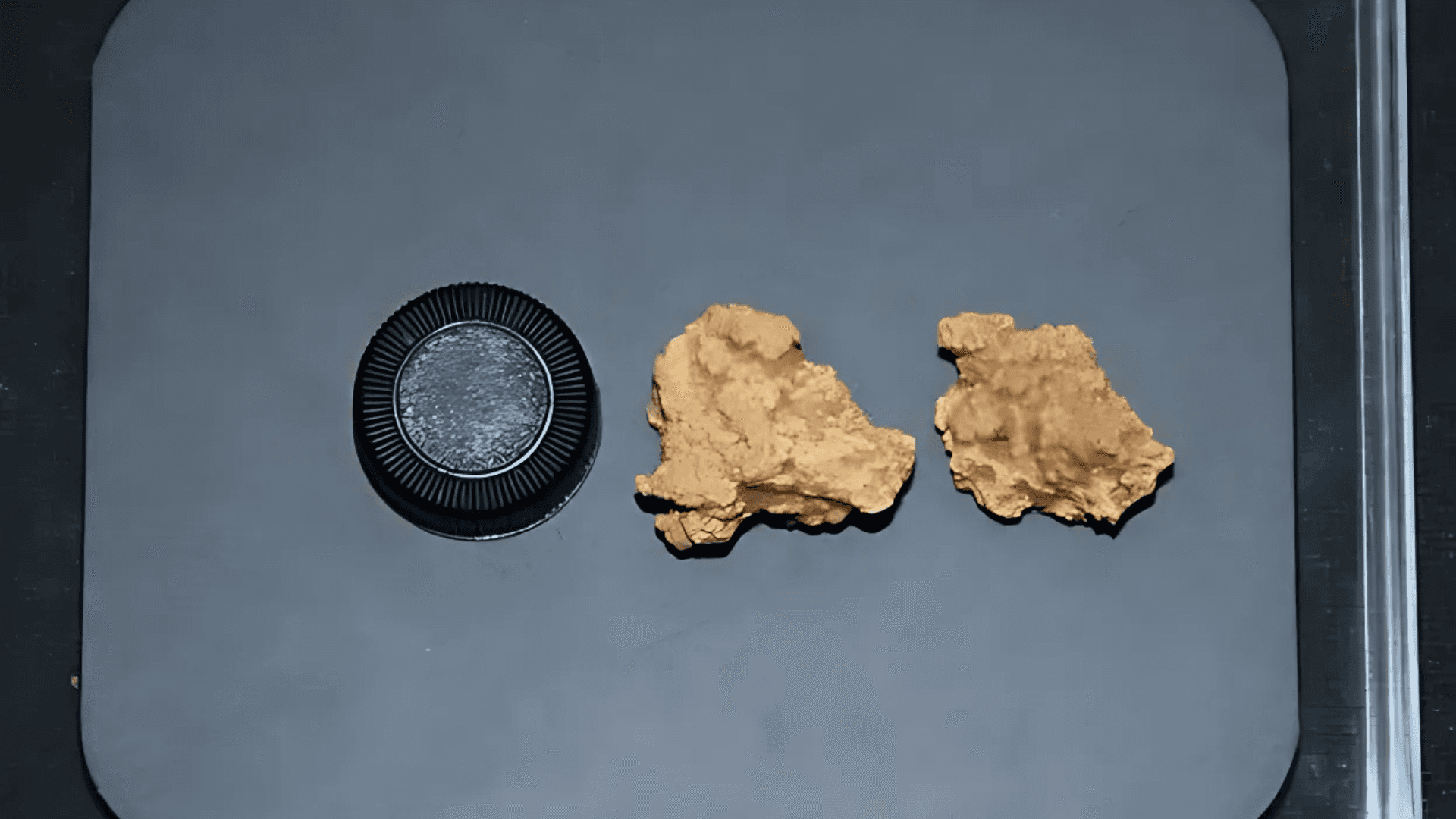

Análisis de ADN en momias chinas de 3.600 años revela el queso más antiguo del mundo
Oct 7, 2024
Estudio revela estabilidad genética de poblaciones del África Austral durante 10 milenios
Oct 4, 2024

Nueve lugares míticos que podrían haber existido, según descubrimientos arqueológicos
Oct 3, 2024
Cómo los derechos humanos pueden salvar los arrecifes de coral y responsabilizar a los gobiernos
Oct 2, 2024

Informe de Carbon Brief señala que 2024 podría ser el año más cálido de la historia
Sep 4, 2024

El clima determina la distribución de mamíferos, revela estudio de la Universidad Estatal de Carolina del Norte
Sep 4, 2024

DeepSeek AI: el chatbot chino que está sacudiendo el mercado global
Feb 7, 2025

Estudio revela que la vida social activa puede reducir el riesgo de demencia
Feb 4, 2025

Año nuevo lunar 2025: la llegada del año de la serpiente
Jan 30, 2025

Nueva hipótesis sobre el origen de los dinosaurios desafía conceptos tradicionales
Jan 27, 2025

Colapso de la plataforma de hielo Conger: alerta para la Antártida Oriental
Dec 20, 2024

Emociones y el cuerpo humano: conexiones milenarias en textos neoasirios
Dec 20, 2024

Un estudio relaciona la contaminación atmosférica con el riesgo de tromboembolia venosa
Dec 20, 2024

Ambiente potencialmente habitable en Marte descubierto por Perseverance
Dec 20, 2024

Revolución XRISM: Nuevos descubrimientos sobre agujeros negros supermasivos
Oct 15, 2024

Estudio aponta que la duplicación del gen AMY1, relacionado con la digestión del almidón, precede a la agricultura
Oct 14, 2024

Nacimientos en la UE caen por debajo de los 4 millones por primera vez desde 1960
Oct 11, 2024

Excavación en Dinamarca revela 50 esqueletos Viking increíblemente preservados
Oct 10, 2024

Estudio detecta mayor incidencia de asma y rinitis alérgica en personas nacidas en otoño e invierno en Finlandia
Oct 9, 2024

Estudio señala similitudes entre la pubertad de adolescentes de la Edad de Hielo y jóvenes modernos
Oct 8, 2024

Análisis de ADN en momias chinas de 3.600 años revela el queso más antiguo del mundo
Oct 7, 2024

Estudio revela estabilidad genética de poblaciones del África Austral durante 10 milenios
Oct 4, 2024

Nueve lugares míticos que podrían haber existido, según descubrimientos arqueológicos
Oct 3, 2024

Cómo los derechos humanos pueden salvar los arrecifes de coral y responsabilizar a los gobiernos
Oct 2, 2024

Informe de Carbon Brief señala que 2024 podría ser el año más cálido de la historia
Sep 4, 2024

El clima determina la distribución de mamíferos, revela estudio de la Universidad Estatal de Carolina del Norte
Sep 4, 2024