Unusual Noise on Boeing's Starliner Puzzles NASA Astronaut
Unusual Noise on Boeing's Starliner Puzzles NASA Astronaut
Unusual Noise on Boeing's Starliner Puzzles NASA Astronaut
Sep 3, 2024
Sep 3, 2024
Sep 3, 2024
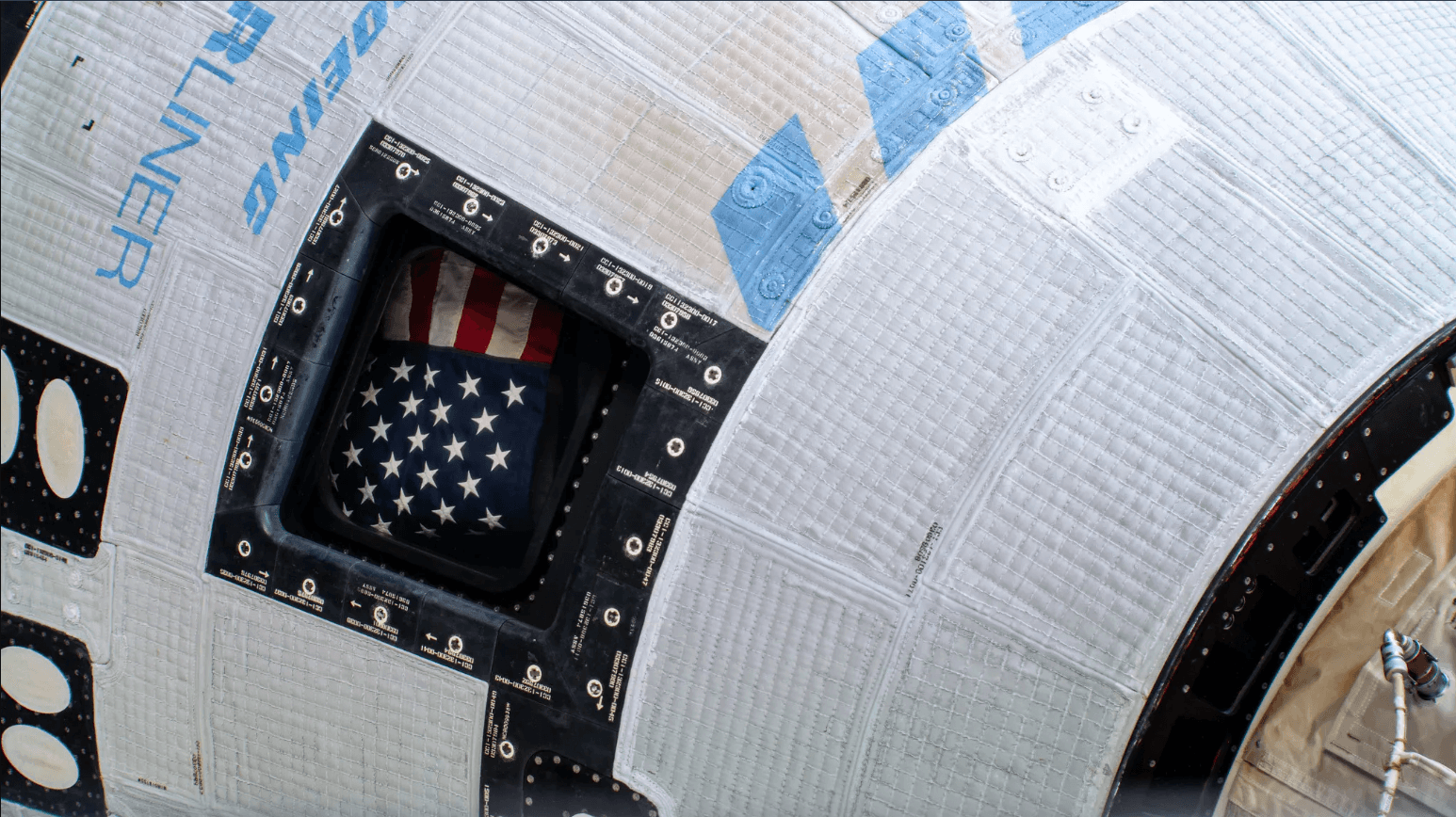
The American flag shown inside the window of Boeing's Starliner spaceship on the International Space Station. Credit: NASA.
The American flag shown inside the window of Boeing's Starliner spaceship on the International Space Station. Credit: NASA.
The American flag shown inside the window of Boeing's Starliner spaceship on the International Space Station. Credit: NASA.
Astronaut Butch Wilmore reports an unusual sound on the Starliner during an ISS mission caused by audio feedback. The incident did not affect mission safety, according to NASA.
Astronaut Butch Wilmore reports an unusual sound on the Starliner during an ISS mission caused by audio feedback. The incident did not affect mission safety, according to NASA.
Astronaut Butch Wilmore reports an unusual sound on the Starliner during an ISS mission caused by audio feedback. The incident did not affect mission safety, according to NASA.
NASA astronaut Butch Wilmore reported hearing an unusual noise coming from Boeing's Starliner spacecraft while it was docked at the International Space Station (ISS). The sound, described as a "pulsing noise" similar to a sonar "ping," caught the attention of the mission control team, who identified the source as an audio feedback issue in the communication system between the Starliner and the ISS.
The Unusual Incident
During his time aboard the ISS, astronaut Butch Wilmore noticed a strange sound coming from the Starliner's audio system. He described the noise as rhythmic, a "pulsing sound" similar to a sonar. Mission control in Houston quickly investigated the case and closely monitored the situation.
NASA's Explanation
According to NASA, the noise was caused by an incorrect configuration in the communication system between the ISS and the Starliner. The agency clarified that the sound did not indicate a technical failure in the spacecraft but came from an audio interference between the two systems. Although unusual, this interference did not pose any risk to the crew or the mission.
Impact on the Mission
Despite the unusual noise, NASA assured that it did not affect the Starliner's operation or compromise astronaut safety. The Starliner is scheduled to undock from the ISS on September 6 and return to Earth unmanned. Experts said the noise was a minor setback in a successful docking and testing mission.
Future of the Starliner
Due to previous issues with the Starliner's thrusters, NASA chose to return astronauts to Earth in a SpaceX Dragon capsule, with the next crewed mission planned for early 2025. Meanwhile, the Starliner will complete its unmanned return, marking another phase in the spacecraft's flight testing.
—
The peculiar noise may have been a minor hiccup, but it highlighted the ongoing technical challenges faced during space missions. As NASA and Boeing continue to monitor and fine-tune the Starliner's performance, incidents like this offer valuable learning opportunities for future manned and unmanned missions. As the Starliner prepares for its return to Earth, progress in space exploration continues, confronting and overcoming unforeseen challenges.
—
Interested in more details about this incident aboard the Starliner? Click here to read the full article that inspired this piece and find out all the information directly from the source.
NASA astronaut Butch Wilmore reported hearing an unusual noise coming from Boeing's Starliner spacecraft while it was docked at the International Space Station (ISS). The sound, described as a "pulsing noise" similar to a sonar "ping," caught the attention of the mission control team, who identified the source as an audio feedback issue in the communication system between the Starliner and the ISS.
The Unusual Incident
During his time aboard the ISS, astronaut Butch Wilmore noticed a strange sound coming from the Starliner's audio system. He described the noise as rhythmic, a "pulsing sound" similar to a sonar. Mission control in Houston quickly investigated the case and closely monitored the situation.
NASA's Explanation
According to NASA, the noise was caused by an incorrect configuration in the communication system between the ISS and the Starliner. The agency clarified that the sound did not indicate a technical failure in the spacecraft but came from an audio interference between the two systems. Although unusual, this interference did not pose any risk to the crew or the mission.
Impact on the Mission
Despite the unusual noise, NASA assured that it did not affect the Starliner's operation or compromise astronaut safety. The Starliner is scheduled to undock from the ISS on September 6 and return to Earth unmanned. Experts said the noise was a minor setback in a successful docking and testing mission.
Future of the Starliner
Due to previous issues with the Starliner's thrusters, NASA chose to return astronauts to Earth in a SpaceX Dragon capsule, with the next crewed mission planned for early 2025. Meanwhile, the Starliner will complete its unmanned return, marking another phase in the spacecraft's flight testing.
—
The peculiar noise may have been a minor hiccup, but it highlighted the ongoing technical challenges faced during space missions. As NASA and Boeing continue to monitor and fine-tune the Starliner's performance, incidents like this offer valuable learning opportunities for future manned and unmanned missions. As the Starliner prepares for its return to Earth, progress in space exploration continues, confronting and overcoming unforeseen challenges.
—
Interested in more details about this incident aboard the Starliner? Click here to read the full article that inspired this piece and find out all the information directly from the source.
NASA astronaut Butch Wilmore reported hearing an unusual noise coming from Boeing's Starliner spacecraft while it was docked at the International Space Station (ISS). The sound, described as a "pulsing noise" similar to a sonar "ping," caught the attention of the mission control team, who identified the source as an audio feedback issue in the communication system between the Starliner and the ISS.
The Unusual Incident
During his time aboard the ISS, astronaut Butch Wilmore noticed a strange sound coming from the Starliner's audio system. He described the noise as rhythmic, a "pulsing sound" similar to a sonar. Mission control in Houston quickly investigated the case and closely monitored the situation.
NASA's Explanation
According to NASA, the noise was caused by an incorrect configuration in the communication system between the ISS and the Starliner. The agency clarified that the sound did not indicate a technical failure in the spacecraft but came from an audio interference between the two systems. Although unusual, this interference did not pose any risk to the crew or the mission.
Impact on the Mission
Despite the unusual noise, NASA assured that it did not affect the Starliner's operation or compromise astronaut safety. The Starliner is scheduled to undock from the ISS on September 6 and return to Earth unmanned. Experts said the noise was a minor setback in a successful docking and testing mission.
Future of the Starliner
Due to previous issues with the Starliner's thrusters, NASA chose to return astronauts to Earth in a SpaceX Dragon capsule, with the next crewed mission planned for early 2025. Meanwhile, the Starliner will complete its unmanned return, marking another phase in the spacecraft's flight testing.
—
The peculiar noise may have been a minor hiccup, but it highlighted the ongoing technical challenges faced during space missions. As NASA and Boeing continue to monitor and fine-tune the Starliner's performance, incidents like this offer valuable learning opportunities for future manned and unmanned missions. As the Starliner prepares for its return to Earth, progress in space exploration continues, confronting and overcoming unforeseen challenges.
—
Interested in more details about this incident aboard the Starliner? Click here to read the full article that inspired this piece and find out all the information directly from the source.
Compartilhar em:
Compartilhar em:
Ver Também
Ver Também

DeepSeek AI: o chatbot chinês que está a sacudir o mercado global
Feb 7, 2025

Estudo revela que uma vida social ativa pode reduzir o risco de demência
Feb 4, 2025

Ano Novo Lunar 2025: a chegada do Ano da Serpente
Jan 30, 2025

Nova hipótese sobre a origem dos dinossauros desafia conceitos tradicionais
Jan 27, 2025

Colapso da plataforma de gelo Conger: alerta para a Antártica Oriental
Dec 20, 2024

Estudo relaciona poluição do ar ao risco de tromboembolismo venoso
Dec 20, 2024

As emoções e o corpo humano: conexões milenares nos textos neo-assírios
Dec 20, 2024
Ambiente potencialmente habitável em Marte é descoberto pelo Perseverance
Dec 20, 2024

Revolução XRISM: novas descobertas sobre buracos negros supermassivos
Oct 15, 2024

Estudo aponta que duplicação do gene AMY1, relacionado à digestão de amido, precede a agricultura
Oct 14, 2024

Nascimentos na UE caem para menos de 4 milhões pela primeira vez desde 1960
Oct 11, 2024

Escavação na Dinamarca revela 50 esqueletos Viking incrivelmente preservados
Oct 10, 2024

Estudo indica maior incidência de asma e rinite alérgica em pessoas nascidas no outono e inverno na Finlândia
Oct 9, 2024

Estudo demonstra semelhanças entre a puberdade de adolescentes da Idade do Gelo e jovens modernos
Oct 8, 2024

Análise de DNA em múmias chinesas de 3.600 anos revela queijo mais antigo do mundo
Oct 7, 2024
Estudo revela estabilidade genética de populações da África Austral por 10 milênios
Oct 4, 2024

Nove lugares míticos que podem ter existido, segundo descobertas arqueológicas
Oct 3, 2024
Como os direitos humanos podem salvar recifes de coral e responsabilizar governos
Oct 2, 2024

Relatório da Carbon Brief aponta que 2024 pode ser o ano mais quente da história
Sep 4, 2024

Clima determina a distribuição de mamíferos, revela estudo da Universidade Estadual da Carolina do Norte
Sep 4, 2024

DeepSeek AI: o chatbot chinês que está a sacudir o mercado global
Feb 7, 2025

Estudo revela que uma vida social ativa pode reduzir o risco de demência
Feb 4, 2025

Ano Novo Lunar 2025: a chegada do Ano da Serpente
Jan 30, 2025

Nova hipótese sobre a origem dos dinossauros desafia conceitos tradicionais
Jan 27, 2025

Colapso da plataforma de gelo Conger: alerta para a Antártica Oriental
Dec 20, 2024

Estudo relaciona poluição do ar ao risco de tromboembolismo venoso
Dec 20, 2024

As emoções e o corpo humano: conexões milenares nos textos neo-assírios
Dec 20, 2024

Ambiente potencialmente habitável em Marte é descoberto pelo Perseverance
Dec 20, 2024

Revolução XRISM: novas descobertas sobre buracos negros supermassivos
Oct 15, 2024

Estudo aponta que duplicação do gene AMY1, relacionado à digestão de amido, precede a agricultura
Oct 14, 2024

Nascimentos na UE caem para menos de 4 milhões pela primeira vez desde 1960
Oct 11, 2024

Escavação na Dinamarca revela 50 esqueletos Viking incrivelmente preservados
Oct 10, 2024

Estudo indica maior incidência de asma e rinite alérgica em pessoas nascidas no outono e inverno na Finlândia
Oct 9, 2024

Estudo demonstra semelhanças entre a puberdade de adolescentes da Idade do Gelo e jovens modernos
Oct 8, 2024

Análise de DNA em múmias chinesas de 3.600 anos revela queijo mais antigo do mundo
Oct 7, 2024

Estudo revela estabilidade genética de populações da África Austral por 10 milênios
Oct 4, 2024

Nove lugares míticos que podem ter existido, segundo descobertas arqueológicas
Oct 3, 2024

Como os direitos humanos podem salvar recifes de coral e responsabilizar governos
Oct 2, 2024

Relatório da Carbon Brief aponta que 2024 pode ser o ano mais quente da história
Sep 4, 2024

Clima determina a distribuição de mamíferos, revela estudo da Universidade Estadual da Carolina do Norte
Sep 4, 2024